其实市面上做接口测试的工具很多,为啥挑这两个来讲解了,重点是真心好用。好了,废话不多说,直接上干货。相信有一定了解的人都知道这两个工具应用最广泛的就是接口测试,既然提到接口测试那我们不得不先普及下什么是接口,接口测试又是啥?我们常说的接口一般指下面两种:
1、API:应用程序编程接口。程序间的接口
· Webservice接口
· RESTful接口
HTTP,RESTful接口走HTTP协议,通过路径来区分调用的方法,请求报文入参有多种形式,返回报文一般为json串,最常见的是get和post方法。
WebService接口是走soap协议,请求报文和返回报文都是xml格式。
而Postman和SopaUI支持的接口类型如下:
因此,我们需要先辨别项目前后端是用何种接口交互再来选取相应的接口测试工具。接口测试又是啥?
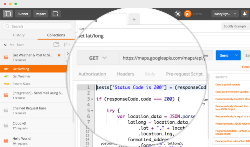
接口测试就是模拟客户端向服务器发送请求报文,服务器接收请求报文后对相应的报文做处理并向客户端返回应答,客户端再接收应答然后对应答做一些校验的过程。
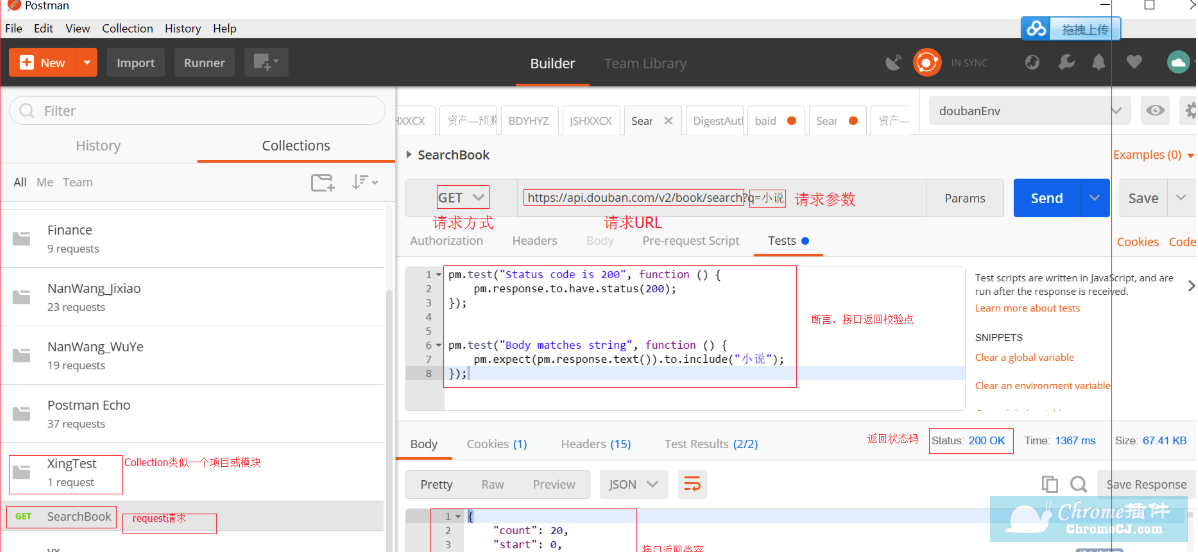
示例:豆瓣公开查找书籍接口
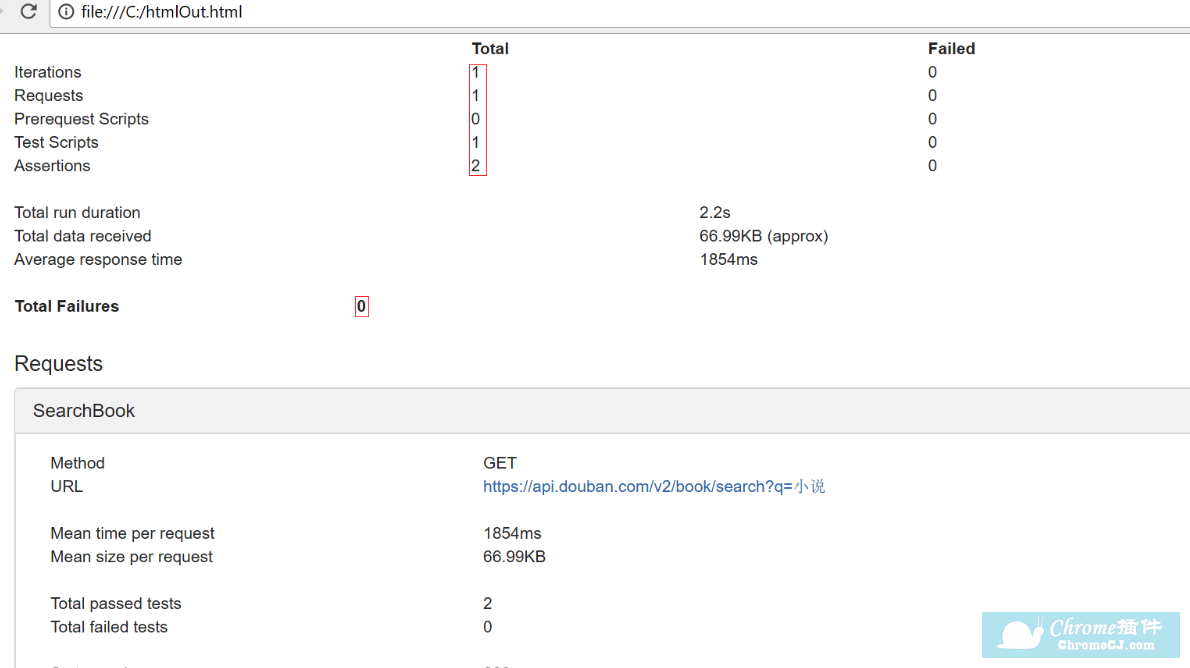
2.导出Collection(项目-接口用例),安装NewMan,用NewManCommand运行Collection并输出HTML报告。
C:\Users\Li.Shi\AppData\Roaming\npm\newmanrunC:\Users\Li.Shi\Desktop\PostMan\LiShiTest.postman_collection.json--reporterscli,json--reporterscli,html--reporter-html-exporthtmlOut.html
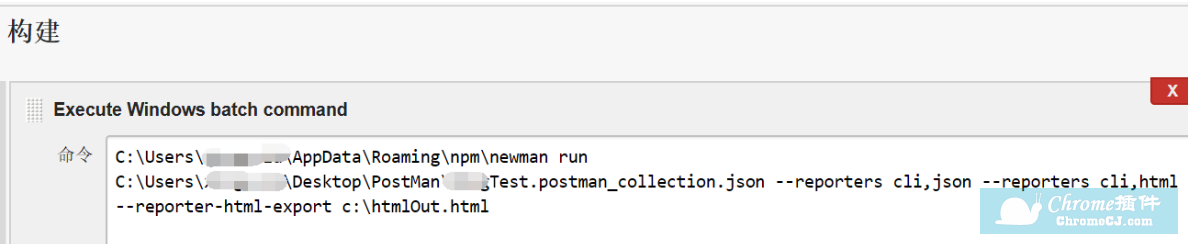
3.安装部署Jenkins,其中Jenkins的配置如下:
至此,我们可完成基于postman和Jenkins的自动化接口测试。
2.用VS(Visual Studio)创建一个Unit Test Project.添加reference,Check System, System.Configuration, System.Core, System.Data
3.添加app config文件,指定soapUI TestRunner.exe所在路径.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="SoapUIHome" value="C:\Program Files\SmartBear\SoapUI-5.3.0\bin"/>
</appSettings>
</configuration>
4.添加SoapUIRunner公共类,通过新建Process去调用TestRunner.exe命令进而运行SoapUI的case.
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace SoapUI
{
public class SoapUIRunner
{
public void RunSoapUItest(string soapProject,string testSuiteName,string testName,string report,string set)
{
const string fileName = "cmd.exe";
var soapProjectFileName = Path.GetFullPath(soapProject);
var arguments = string.Format("/C testrunner.bat -s\"{0}\" -c\"{1}\" \"{2}\" -r -a -f\"{3}\" -t\"{4}\" ", testSuiteName, testName, soapProjectFileName, report, set);
var soapHome = System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["SoapUIHome"];
//start a process and hook up the in/output
var process = new Process
{
StartInfo = new ProcessStartInfo
{
FileName = fileName,
Arguments = arguments,
WorkingDirectory = soapHome,
Verb = "runas",
CreateNoWindow = true,
ErrorDialog = false,
RedirectStandardError= true,
RedirectStandardOutput = true,
UseShellExecute = false
},
EnableRaisingEvents = true
};
//pipe the output to console.writeline
process.OutputDataReceived += (sender, args) =>
Console.WriteLine(args.Data);
var errorBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//store the errors in a stringbuilder
process.ErrorDataReceived += (sender, args) =>
{
if (args != null && args.Data != null)
{
errorBuilder.AppendLine(args.Data);
}
};
process.Start();
process.BeginOutputReadLine();
process.BeginErrorReadLine();
//wait for soapUI to finish
process.WaitForExit();
//fail the test if anything fails
var errorMessage = errorBuilder.ToString();
if(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(errorMessage))
{
Assert.Fail("Test with name '{0}' failed. {1} {2}", testName, Environment.NewLine, errorMessage);
}
}
}
}
5.通过Unit Test调用SoapUI TestSuit, 进而可以运用bat命令集成运行TestCase. 做到接口的自动化测试。
using System;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
namespace SoapUI
{
[TestClass]
[DeploymentItem(@"soapUIFiles\DeviceReportService-soapui-project.xml", "TestData\\soapUIFiles")]
public class DeviceReport:SoapUIRunner
{
private string testCaseSuiteName = "BasicHttpBinding_DeviceReport TestSuite";
private string soapProjectFile= @"TestData\\soapUIFiles\\DeviceReportService-soapui-project.xml";
private string reportFile = @"C:\Users\" + Environment.UserName + "\\Desktop\\TestReport";
private String SoapUISettingsFile = @"TestData\\soapUIFiles\\soapui-settings.xml";
private TestContext testContext;
public TestContext TestContext
{
get { return this.testContext; }
set { this.testContext = value; }
}
[TestMethod]
[TestCategory("DeviceReport")]
public void Device_Report()
{
RunSoapUItest(soapProjectFile, testCaseSuiteName, "DeviceReport TestCase", reportFile, SoapUISettingsFile);
}
}
}
2.从两种工具用例组织方式来看:
SoapUI的组织方式如下图,最上层是WorkSpace,所以每个WorkSpace中可以打开多个Project,一个Project也可以在不同的WorkSpace中。
Project对应我们的测试项目,其中可添加WSDL、WADL资源、TestSuite以及MockService。
TestSuite对应我们的测试模块,比如商户中心,其中可以添加TestCase,TestCase对应我们对某个模块的不同接口,比如订单管理接口。而一个接口可以能需要多个Step完成,变量、数据源、请求等都是一个Step。
Postman功能上更简单,组织方式也更轻量级,它主要针对的就是单个的HTTP请求。Collection就相当于是Project,而Collection中可以创建不定层级的Folders,可以自己组织TestSuite。每个Request可以当做是一个TestCase或者Step:
3.从长期的团队协作来看:
SoapUI:本身一个project是一个xml文件,但是可以通过配置变成一系列文件夹,每个Case、每个Suite均是独立的文件,这样可通过svn/git/TFS进行团队协作。支持性较好。
Postman:有团队协作的功能,需要付费。
因此从项目支持的接口类型,不同集成测试需求和后期维护来考虑,我们可以根据上面几点选择适合自己项目的接口自动化工具。
1、API:应用程序编程接口。程序间的接口
2、GUI:图形用户界面。人与程序的接口

我们这里说的接口测试主要指API接口测试,API接口分类一般有如下几种:
· HTTP接口· Webservice接口
· RESTful接口
HTTP,RESTful接口走HTTP协议,通过路径来区分调用的方法,请求报文入参有多种形式,返回报文一般为json串,最常见的是get和post方法。
WebService接口是走soap协议,请求报文和返回报文都是xml格式。
而Postman和SopaUI支持的接口类型如下:
因此,我们需要先辨别项目前后端是用何种接口交互再来选取相应的接口测试工具。接口测试又是啥?
接口测试就是模拟客户端向服务器发送请求报文,服务器接收请求报文后对相应的报文做处理并向客户端返回应答,客户端再接收应答然后对应答做一些校验的过程。
下面我们分别介绍下如何用PostMan和SoapUI做接口自动化测试。
A:Postman+Newman+Jenkins实现接口自动化测试
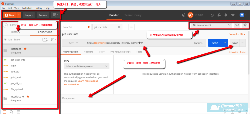
1.安装Postman,编写API接口测试用例示例:豆瓣公开查找书籍接口

2.导出Collection(项目-接口用例),安装NewMan,用NewManCommand运行Collection并输出HTML报告。
C:\Users\Li.Shi\AppData\Roaming\npm\newmanrunC:\Users\Li.Shi\Desktop\PostMan\LiShiTest.postman_collection.json--reporterscli,json--reporterscli,html--reporter-html-exporthtmlOut.html

3.安装部署Jenkins,其中Jenkins的配置如下:

至此,我们可完成基于postman和Jenkins的自动化接口测试。
B:SoapUI+UnitTest 实现接口自动化测试
1.安装SoapUI,自行创建一个可运行的SoapUI的Project,得到项目XML文件.eg:DeviceReportService-soapui-project.xml2.用VS(Visual Studio)创建一个Unit Test Project.添加reference,Check System, System.Configuration, System.Core, System.Data
3.添加app config文件,指定soapUI TestRunner.exe所在路径.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="SoapUIHome" value="C:\Program Files\SmartBear\SoapUI-5.3.0\bin"/>
</appSettings>
</configuration>
4.添加SoapUIRunner公共类,通过新建Process去调用TestRunner.exe命令进而运行SoapUI的case.
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace SoapUI
{
public class SoapUIRunner
{
public void RunSoapUItest(string soapProject,string testSuiteName,string testName,string report,string set)
{
const string fileName = "cmd.exe";
var soapProjectFileName = Path.GetFullPath(soapProject);
var arguments = string.Format("/C testrunner.bat -s\"{0}\" -c\"{1}\" \"{2}\" -r -a -f\"{3}\" -t\"{4}\" ", testSuiteName, testName, soapProjectFileName, report, set);
var soapHome = System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["SoapUIHome"];
//start a process and hook up the in/output
var process = new Process
{
StartInfo = new ProcessStartInfo
{
FileName = fileName,
Arguments = arguments,
WorkingDirectory = soapHome,
Verb = "runas",
CreateNoWindow = true,
ErrorDialog = false,
RedirectStandardError= true,
RedirectStandardOutput = true,
UseShellExecute = false
},
EnableRaisingEvents = true
};
//pipe the output to console.writeline
process.OutputDataReceived += (sender, args) =>
Console.WriteLine(args.Data);
var errorBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//store the errors in a stringbuilder
process.ErrorDataReceived += (sender, args) =>
{
if (args != null && args.Data != null)
{
errorBuilder.AppendLine(args.Data);
}
};
process.Start();
process.BeginOutputReadLine();
process.BeginErrorReadLine();
//wait for soapUI to finish
process.WaitForExit();
//fail the test if anything fails
var errorMessage = errorBuilder.ToString();
if(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(errorMessage))
{
Assert.Fail("Test with name '{0}' failed. {1} {2}", testName, Environment.NewLine, errorMessage);
}
}
}
}
5.通过Unit Test调用SoapUI TestSuit, 进而可以运用bat命令集成运行TestCase. 做到接口的自动化测试。
using System;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
namespace SoapUI
{
[TestClass]
[DeploymentItem(@"soapUIFiles\DeviceReportService-soapui-project.xml", "TestData\\soapUIFiles")]
public class DeviceReport:SoapUIRunner
{
private string testCaseSuiteName = "BasicHttpBinding_DeviceReport TestSuite";
private string soapProjectFile= @"TestData\\soapUIFiles\\DeviceReportService-soapui-project.xml";
private string reportFile = @"C:\Users\" + Environment.UserName + "\\Desktop\\TestReport";
private String SoapUISettingsFile = @"TestData\\soapUIFiles\\soapui-settings.xml";
private TestContext testContext;
public TestContext TestContext
{
get { return this.testContext; }
set { this.testContext = value; }
}
[TestMethod]
[TestCategory("DeviceReport")]
public void Device_Report()
{
RunSoapUItest(soapProjectFile, testCaseSuiteName, "DeviceReport TestCase", reportFile, SoapUISettingsFile);
}
}
}
接下来我们对比下用方式A和B做接口自动化的区别:
1.从上面的实现来看,SoapUI自动化需要测试人员有一定的编码能力,想比如Postman会对测试人员要求高些。2.从两种工具用例组织方式来看:
SoapUI的组织方式如下图,最上层是WorkSpace,所以每个WorkSpace中可以打开多个Project,一个Project也可以在不同的WorkSpace中。
Project对应我们的测试项目,其中可添加WSDL、WADL资源、TestSuite以及MockService。
TestSuite对应我们的测试模块,比如商户中心,其中可以添加TestCase,TestCase对应我们对某个模块的不同接口,比如订单管理接口。而一个接口可以能需要多个Step完成,变量、数据源、请求等都是一个Step。
Postman功能上更简单,组织方式也更轻量级,它主要针对的就是单个的HTTP请求。Collection就相当于是Project,而Collection中可以创建不定层级的Folders,可以自己组织TestSuite。每个Request可以当做是一个TestCase或者Step:
3.从长期的团队协作来看:
SoapUI:本身一个project是一个xml文件,但是可以通过配置变成一系列文件夹,每个Case、每个Suite均是独立的文件,这样可通过svn/git/TFS进行团队协作。支持性较好。
Postman:有团队协作的功能,需要付费。
因此从项目支持的接口类型,不同集成测试需求和后期维护来考虑,我们可以根据上面几点选择适合自己项目的接口自动化工具。
查看更多


 4.6 分
4.6 分
 4.3 分
4.3 分



















 3.2 分
3.2 分